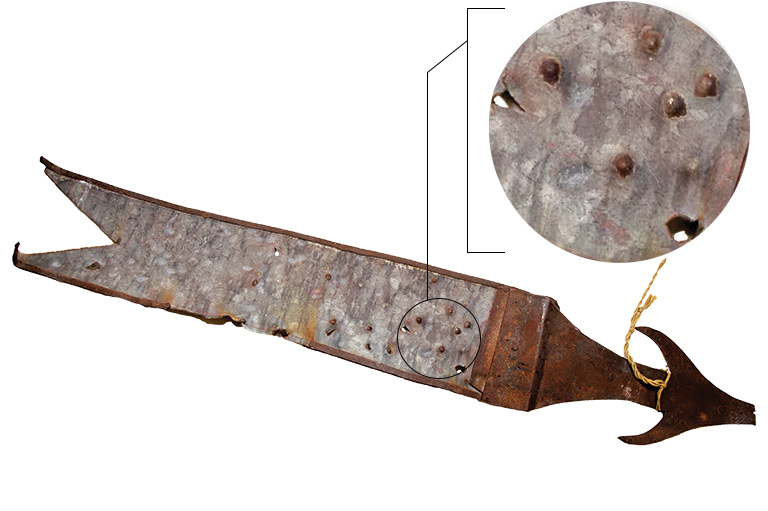
Astrolabe
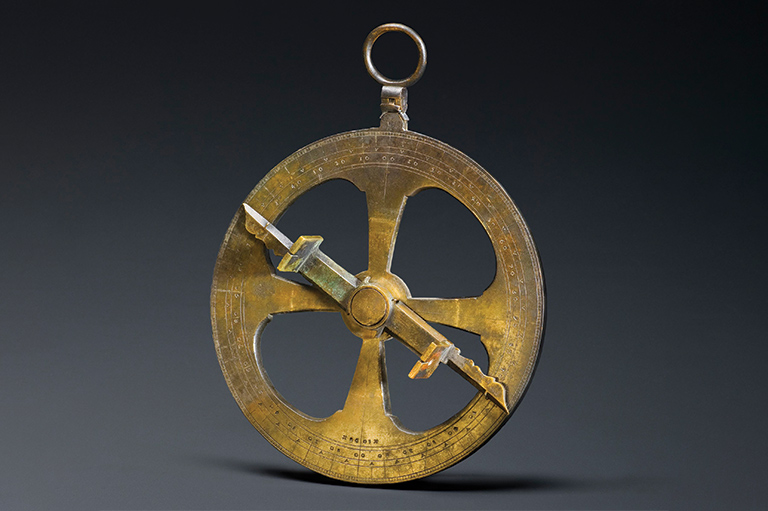

This astrolabe, dated 1603, is usually attributed to the French explorer and cartographer Samuel de Champlain. It was discovered in 1867 near the Ottawa River. This navigation instrument allows the user to determine his location by measuring the position of the sun, the moon, and the stars.
Champlain certainly possessed such an object. He would have used it to cross Atlantic Ocean, when he was appointed by the King of France to search for a westward route to China and the Indies. Champlain made twelve trips to North America between 1603 and 1635, and explored the northeast coast of Canada and the St. Lawrence River. He certainly used an astrolabe such as this to map the places he explored.
During his third trip in 1608, he founded the colony of Quebec, which became the first permanent French settlement in North America, on the site of the former Indigenous village of Stadacona. The Iroquoian inhabitants had abandoned the site for reasons that might have included wars, epidemics, and failed harvests.
Champlain decided to establish his colony at the site due to its proximity to fur trade routes. In addition, the high cliffs at Cap Diamant provided an excellent defensive position and allowed the French colonists to monitor the movement of watercraft on the St. Lawrence River. Finally, Champlain believed the site’s fertile soils and relatively temperate climate gave it a certain agricultural potential, which would allow settlers to become self-sufficient.
With 7 uniquely curated newsletters to choose from, we have something for everyone.
Themes associated with this article
Advertisement